Leading the Circular Economy/Winner category
The Green Trench Innovation Alliance, led by Victoria University in collaboration with Greater Western Water and Ground Science, is revolutionising how trench infrastructure is delivered in Australia. This award-winning project developed and trialled two high-performance backfill blends made entirely from recycled glass, plastic, rubber, and crushed concrete. Piloted on live construction sites, these blends replaced virgin materials, reduced carbon emissions, and delivered cost savings—proving that circular economy solutions can outperform traditional approaches. With embedded monitoring, mobile batching, and multi-stakeholder engagement, the project has already begun influencing national standards and presents a scalable model for low-carbon infrastructure transformation.

Environmental and Social Benefits
- The recycled blends divert over 250 tonnes of virgin aggregate and save more than 280 tonnes of CO₂ emissions per 100m of trenching, significantly lowering the environmental footprint of civil works.
- The project repurposes challenging waste streams—including glass fines, soft plastics, crumb rubber and crushed concrete—into functional infrastructure inputs, helping address regional landfill pressures and material shortages.
- Students gained hands-on experience in live construction environments, while local suppliers and councils benefited from knowledge-sharing and material reuse pathways.
Leadership and Engagement
- Green Trench is the first project in Australia to test fully recycled backfill materials under real construction conditions, providing practical evidence of performance and viability.
- Contractors, suppliers, water authorities and academics co-designed the blends and monitoring protocols, ensuring solutions met both technical and operational requirements.
- Over 30 stakeholders contributed, including undergraduate students, PhD researchers, utilities, civil engineers, and local government representatives—fostering deep industry-academic integration.
Significance to the Sector
- The success of Green Trench has informed upcoming revisions to AS/NZS 3725, shifting industry expectations of what’s possible in trench backfill performance and sustainability.
- The mobile batching process and use of low-cost recycled inputs proved that sustainable materials can meet price, performance and policy requirements—without compromising delivery.
- Green Trench moves beyond pilots and prototypes, offering a tested, transferable model for circular practices in civil works, utilities and public infrastructure.
Wider Societal Impact
- Supports climate-resilient and resource-efficient infrastructure that benefits communities long-term.
- Strengthens circular economy supply chains and local industry capabilities, especially in regional areas.
- Positions universities as key innovators in low-carbon construction and practical systems change.
Top 3 learnings
Category finalists
Staff Champion/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Benefitting Society/Winner
Benefitting Society/Winner
Creating Impact/Winner
Creating Impact/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy
Leading the Circular Economy
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winner
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy/Winner
Diversity Equity & Inclusion/Winner
Diversity Equity & Inclusion/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Sustainability Leadership/Winner
Sustainability Leadership/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy
Leading the Circular Economy
Student Champion/Winner
Student Champion/Winner
Student Engagement/Winner
Student Engagement/Winner
Past winners
Benefitting Society/Winners
Benefitting Society/Winners
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion in Sustainability/Winners
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion in Sustainability/Winners
Climate Action/Winners
Climate Action/Winners
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winners
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winners
Creating Impact/Winners
Creating Impact/Winners
Creating Impact/Winners
Creating Impact/Winners
Top 3 learnings
Leading the Circular Economy/Winner category
The Green Trench Innovation Alliance, led by Victoria University in collaboration with Greater Western Water and Ground Science, is revolutionising how trench infrastructure is delivered in Australia. This award-winning project developed and trialled two high-performance backfill blends made entirely from recycled glass, plastic, rubber, and crushed concrete. Piloted on live construction sites, these blends replaced virgin materials, reduced carbon emissions, and delivered cost savings—proving that circular economy solutions can outperform traditional approaches. With embedded monitoring, mobile batching, and multi-stakeholder engagement, the project has already begun influencing national standards and presents a scalable model for low-carbon infrastructure transformation.

Environmental and Social Benefits
- The recycled blends divert over 250 tonnes of virgin aggregate and save more than 280 tonnes of CO₂ emissions per 100m of trenching, significantly lowering the environmental footprint of civil works.
- The project repurposes challenging waste streams—including glass fines, soft plastics, crumb rubber and crushed concrete—into functional infrastructure inputs, helping address regional landfill pressures and material shortages.
- Students gained hands-on experience in live construction environments, while local suppliers and councils benefited from knowledge-sharing and material reuse pathways.
Leadership and Engagement
- Green Trench is the first project in Australia to test fully recycled backfill materials under real construction conditions, providing practical evidence of performance and viability.
- Contractors, suppliers, water authorities and academics co-designed the blends and monitoring protocols, ensuring solutions met both technical and operational requirements.
- Over 30 stakeholders contributed, including undergraduate students, PhD researchers, utilities, civil engineers, and local government representatives—fostering deep industry-academic integration.
Significance to the Sector
- The success of Green Trench has informed upcoming revisions to AS/NZS 3725, shifting industry expectations of what’s possible in trench backfill performance and sustainability.
- The mobile batching process and use of low-cost recycled inputs proved that sustainable materials can meet price, performance and policy requirements—without compromising delivery.
- Green Trench moves beyond pilots and prototypes, offering a tested, transferable model for circular practices in civil works, utilities and public infrastructure.
Wider Societal Impact
- Supports climate-resilient and resource-efficient infrastructure that benefits communities long-term.
- Strengthens circular economy supply chains and local industry capabilities, especially in regional areas.
- Positions universities as key innovators in low-carbon construction and practical systems change.
Related finalists
Staff Champion/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Benefitting Society/Winner
Benefitting Society/Winner
Creating Impact/Winner
Creating Impact/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Staff Champion/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy
Leading the Circular Economy
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winner
Sustainability Institution of the Year/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy/Winner
Diversity Equity & Inclusion/Winner
Diversity Equity & Inclusion/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Sustainability Leadership/Winner
Sustainability Leadership/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Nature Positive/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Next Generation Learning & Skills/Winner
Leading the Circular Economy
Leading the Circular Economy
Student Champion/Winner
Student Champion/Winner
Student Engagement/Winner
Student Engagement/Winner
Other finalists
Climate Action
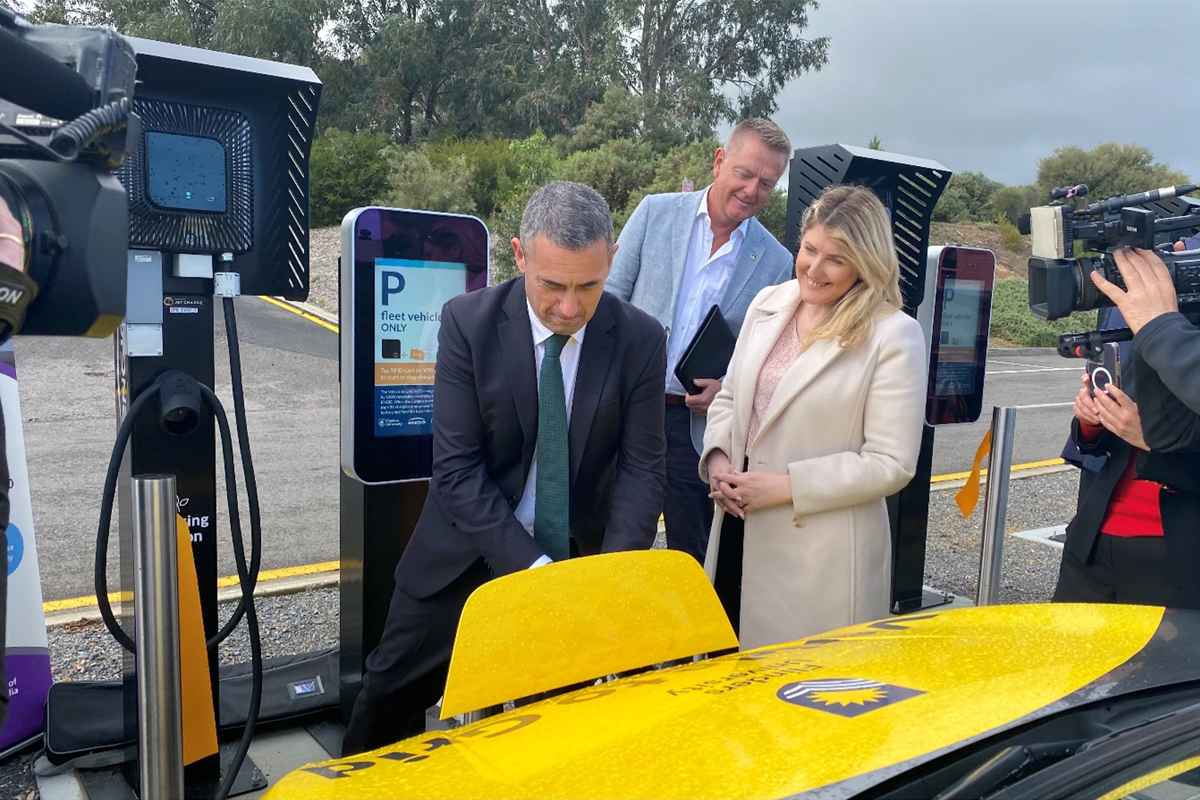

Driving Towards Tomorrow’s Campus with Vehicle-to-Grid EV Technology
As part of Flinders University’s drive to innovate and become a leader in climate action, the University launched its Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) initiative. This involved installing and maintaining 20x V2G and smart chargers for its growing electric vehicle fleet. Leveraging 100% renewable energy generated by ENGIE’s Willogoleche Wind Farm and Flinders University’s solar power systems, this enables the storage of renewable energy in EV batteries to be discharged on campus during peak demand periods. Hence, allows for these EV fleets to operate as a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) to deliver peak demand management and optimization of behind-the-meter generation.
Overall, this initiative demonstrates the reliability and scalability of bi-directional and uni-directional smart-charging systems for EVs in reducing GHG emissions while facilitating teaching, research, and innovation opportunities. Moreover, it exemplifies a sustainable and innovative solution to scale energy storage technology and increase renewables.
Sustainability Champion – Staff/Winners
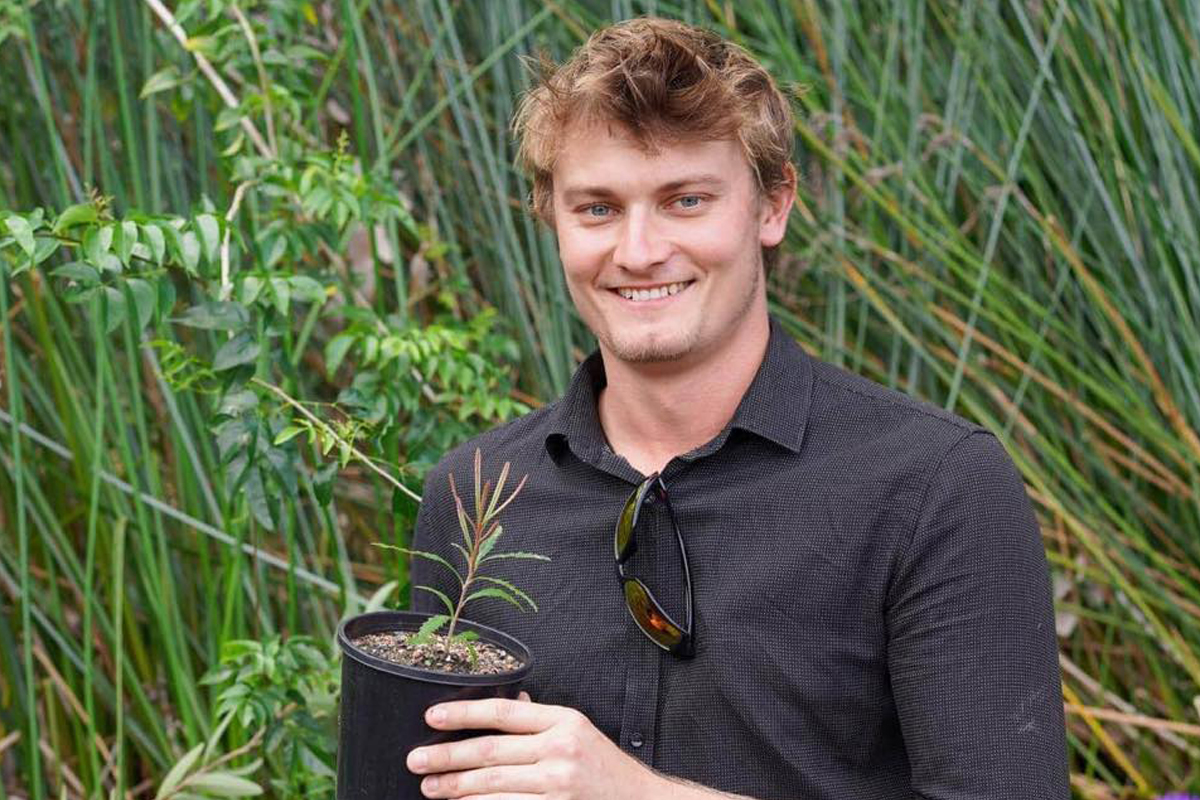

Brandan Espe
Environmental Officer / Acting Grounds Supervisor
Brandan has brought over 50 federally listed Endangered species of plant into the James Cook University living collection, many of which have never been cultivated and are found in no other collection in the world.
Of these, over half have been sustainably wild collected, inclusive of field and clone data, so they can be used for ongoing conservation, research and teaching, the remaining being sourced from private and partner organisations through favours of service or trades.
He personally funded the project from 2019-2022, until funding was awarded for the program due to its success, with the program now being engrained into the Universities landscapes for ongoing management should he leave JCU, creating a threatened species legacy collection.
The program has now expanded beyond this, with an additional 48 species now funded for further addition, some of which are only known from less than 5 sightings in history.
Student Engagement
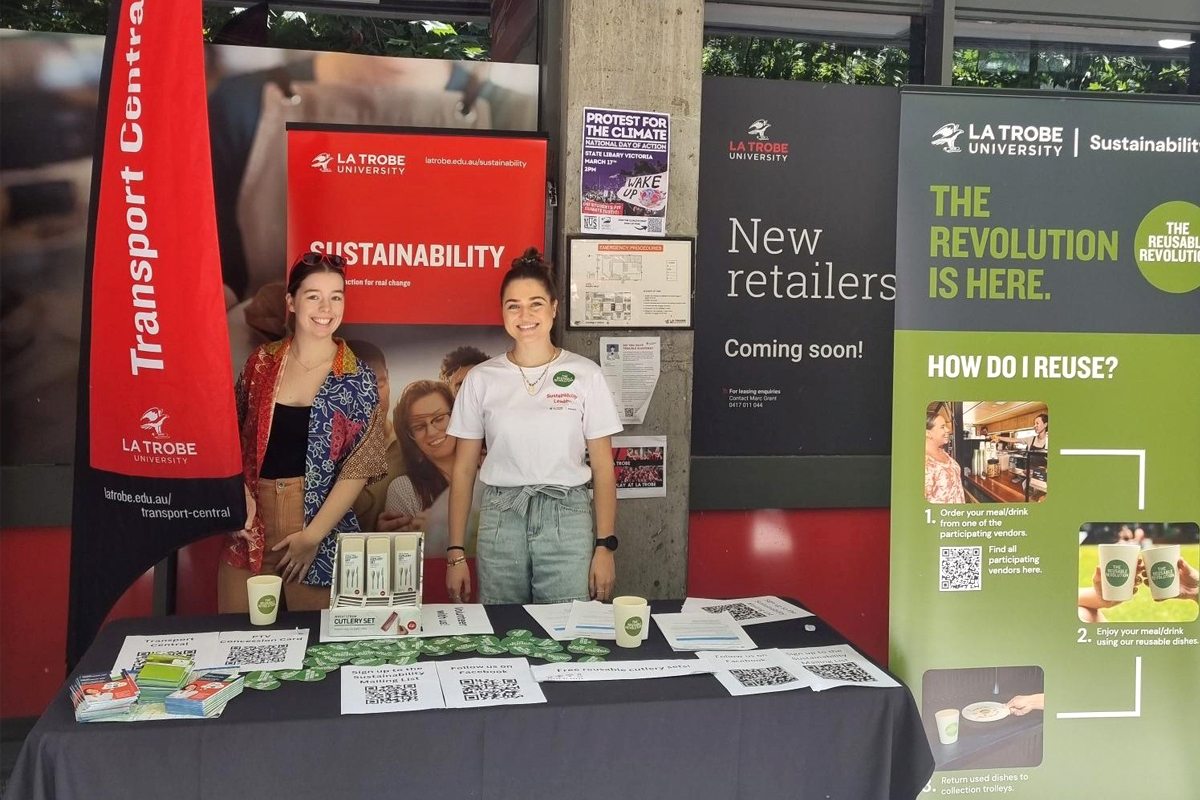

Sustainability Leaders creating real impact!
La Trobe created a unique Sustainability Leaders volunteering program to increase engagement with students on campus and empower them to act against waste and promote sustainability. It included the following initiatives:
- Promoting the reusable crockery implementation,
- Increasing knowledge action of other students on campus to diversion comingled recycling and organic waste from landfill.
- Focus on waste audits and data,
- Improved signage through new waste posters for students living on campus.
- Collaboration with Cirka (our cleaning and waste partner) to create a waste wall and;
- Learning all things sustainability (net zero, biodiversity, waste, reusables, engagement)
These initiatives yielded significant results and with a reduction in waste contamination by almost 40% at the residential buildings and engagement with over 80 groups of people for the Reusable Revolution.
Creating Impact
Where knowledge meets habits: Empowering students for a sustainable tomorrow
Our online Sustainability Challenges offer participants an engaging, self-paced learning experience centered around a specific United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (UNSDG). Requiring minimal resourcing and at zero-cost to participants, we’ve created replicable, compact, scalable, and impactful learning opportunities that result in real impact.
The Challenges follow a structured process that moves participants from knowledge gain to simple action to celebration, to establish small but mighty habits relating to waste and carbon emissions. This approach recognises that knowledge alone is often insufficient to drive behaviour change, and that ease of action and celebration are crucial components in creating sustainable habits.
Sustainability Champion – Staff/Winners
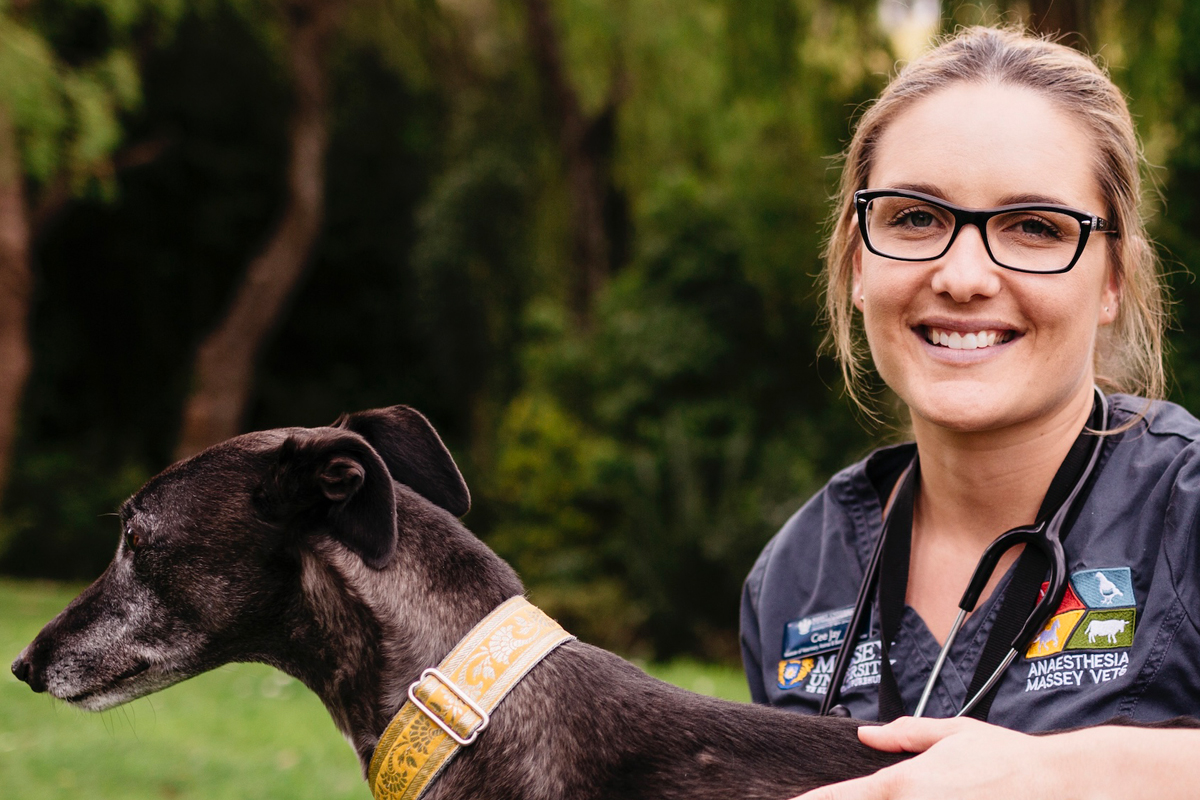

Catherine (CeeJay) Donovan
Veterinary nurse – Anaesthesia
From establishing the Massey Vet School Green Team to leading impactful initiatives, my commitment to environmental sustainability has been making waves. With the help of my team, I have accomplished numerous small, yet meaningful actions, including integrating a sustainability lecture for final year vet students and implementing battery recycling alongside rechargeable battery use. Our larger projects encompass the introduction of green waste and soft plastics recycling bins, an energy audit resulting in power-saving measures, and playing a part in a successful rubbish audit. I spearheaded the ‘6 in 6’ campaign, empowering individuals with six simple steps for workplace sustainability. Through the SustainaVet social media pages I help to educate and inspire peers nationwide. As the Massey School of Veterinary Science sustainability champion, I had the privilege of speaking at the annual veterinary conference on sustainability in clinical practice. Currently I’m conducting pioneering research on responsible cat waste disposal. Together, we’re forging a greener future, one initiative at a time.
Sustainability Champion – Student
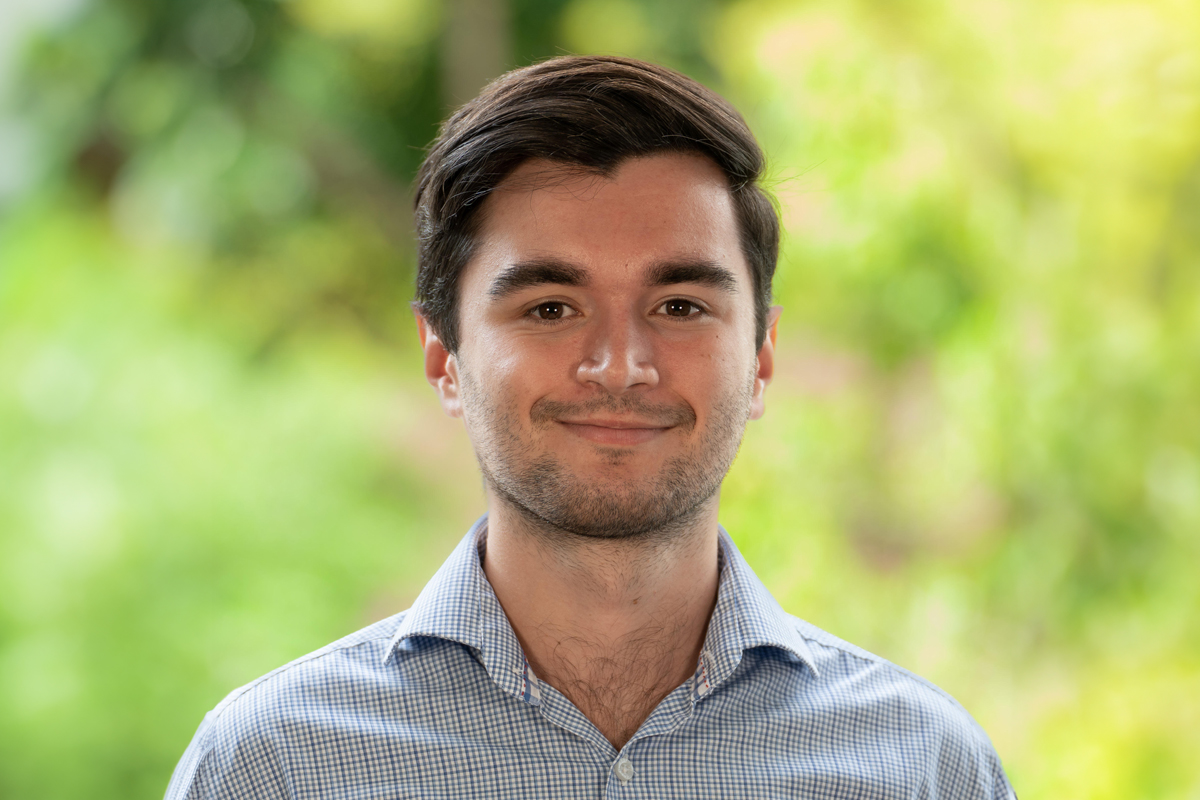

Louis Walmsley
SDG Coordinator Monash Association of Sustainability, Office Bearer Monash Student Association’s Environmental and Social Justice Department, Masters of Environment and Sustainability Student
Louis is an exceptional student sustainability leader at Monash University. His passion and dedication to sustainability have made a significant impact on the community. Louis’s values revolve around sustainability, which is evident upon meeting him. He actively participates in various sustainability groups, demonstrating his commitment to creating a more environmentally conscious society.
One of Louis’s notable involvements is with Precious Plastic Monash, where he organizes remarkable events and fosters collaboration among like-minded individuals, student groups, and staff. His contributions to the Monash Association of Sustainability have allowed him to conduct valuable research on plastic usage and climate action, resulting in positive changes within the university.
Through his work with the Monash Student Association, Louis has engaged hundreds of students in fun and interactive sustainability initiatives. He took the initiative to organize a sustainability food fair, which was one of the largest sustainability-related events held at Monash post-COVID. This accomplishment is a true testament to Louis’s hard work and creativity.
Louis is an outstanding student leader whose efforts in sustainability have had a lasting impact on Monash University and its community. His inspiring nature resonates with everyone who knows him.






























